
If you want to play games on your computer or run graphics-intensive software like Adobe Photoshop or illustrator, you need a powerful-enough GPU. To determine whether your current graphics card can run the latest games or particular software, you'll need to ask yourself "what graphics card do I have?" and "what are its specs?".
In this blog post, I'm going to walk you through how to find out the make, model, and specs of your graphics card in windows, macOS, and Linux.
Contents
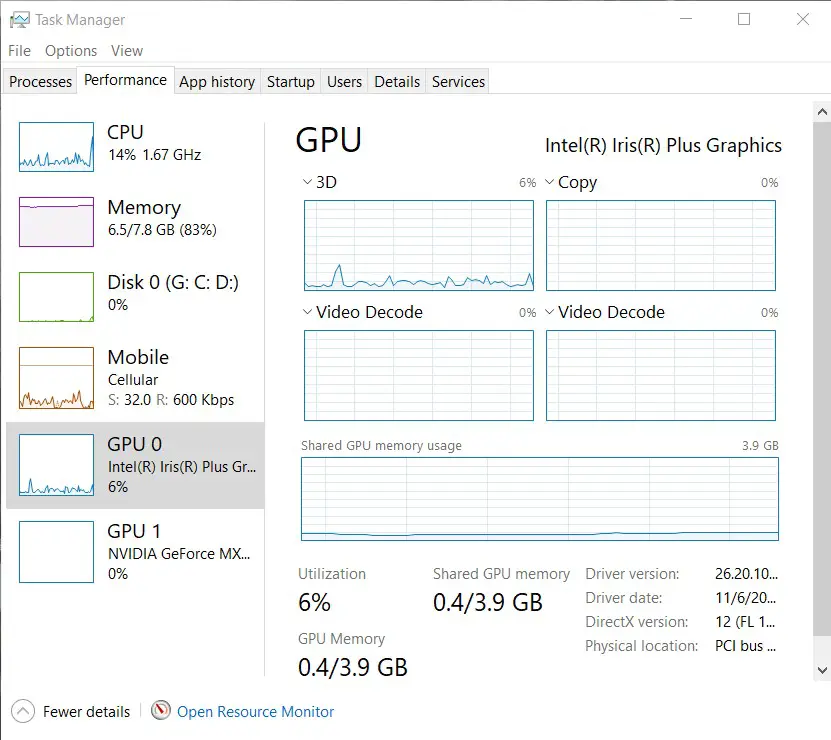
If you want to view GPU usage on Windows 10, you can do so using the task manager. However, you’ll first have to enable this information since it’s hidden by default:
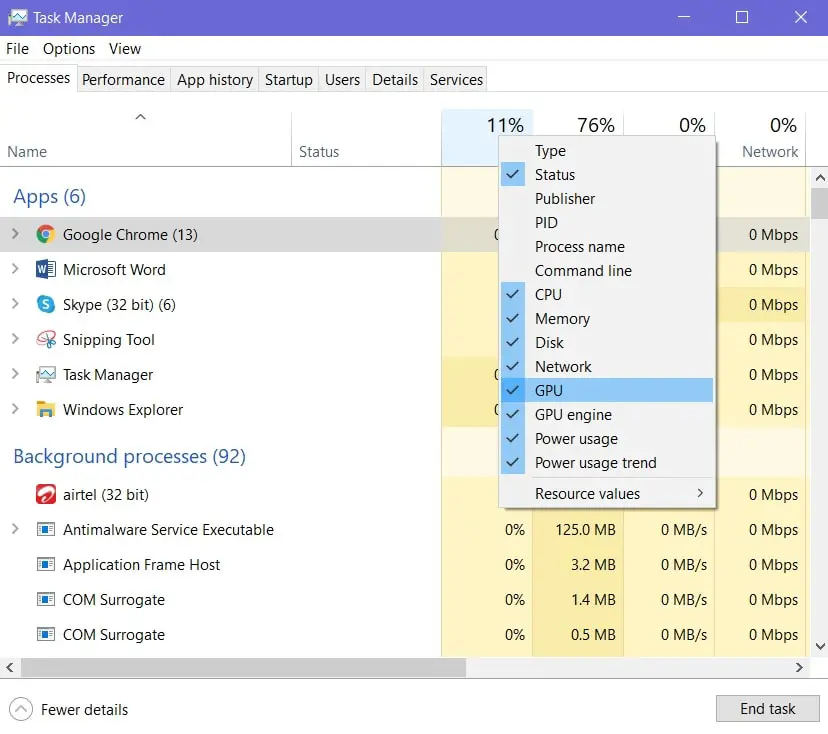
Note: GPU monitoring features are only available for Windows 10 version 1709. If you want to check which version of Windows 10 is installed on your computer, check out this handy guide from HowToGeek.
How to check GPU Usage Windows 7
Unfortunately, there's no built-in GPU usage monitoring feature in the Windows 7 task manager. Hence, you'll have to rely on a third-party tool like GPU-Z.
GPU-Z is windows-exclusive software made by TechPowerUp which gives you GPU usage readings. It works with NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel GPUs.
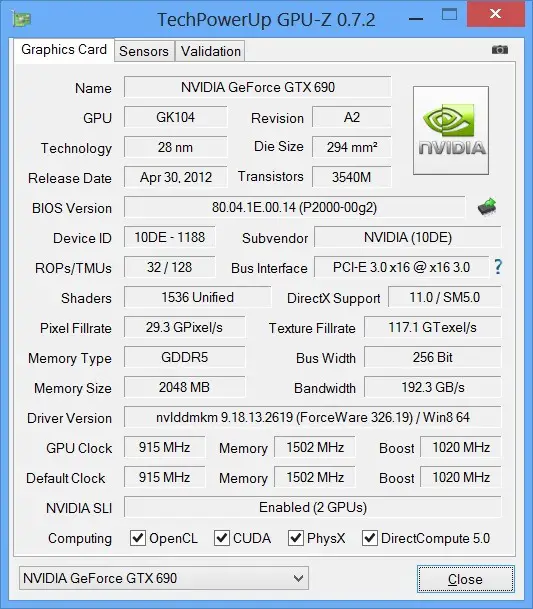
This tool is incredibly easy to use. So easy in fact that you don't even have to install it. Just download and run it. When you launch GPU-Z, you'll see the below interface which lists all the technical specs of your GPU.
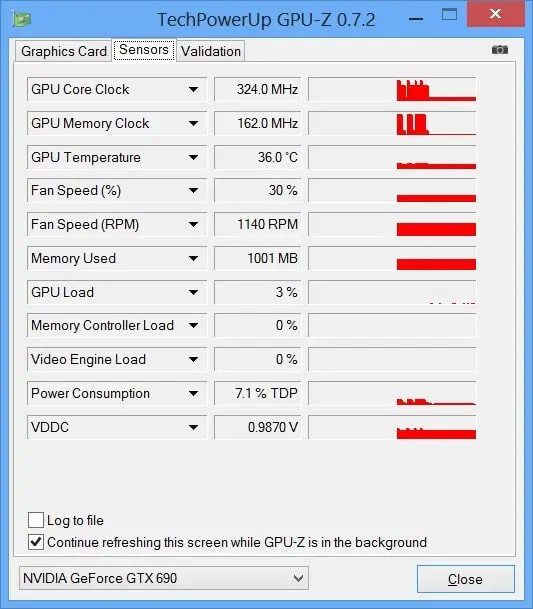
If you want to monitor usage, switch to the Sensors tab.
And that’s everything you need to know on how to check graphics card on pc. Let’s move on to the other two operating systems.
How do I detect my video card on MacOS? Here’s the short and easy way:
And that’s all you have to do to identify the graphics card installed on a Mac.
Here are simple instructions on how to check graphics card info on a Linux Machine.
1. To start with, open up the Terminal. You can either click on the Terminal app icon or use the Keyboard shortcut: Alt, control, and T pressed together.
2. On the terminal, type in the following command after the prompt: sudo update pciids.
This will update the list your computer has on the installed PCI items (i.e components mounted on PCI slots).
3. You will be prompted to enter your password since your issuing an administrative command (sudo). This is the same password that you use to log into your computer. The PCI list will now be updated.
4. You can now look up the list of PCI items. Simply type in the following command to bring it up: lspci -v | less.
5. Scroll through the list until you come across one of the following headings:
6. You'll find the name of your graphics card next to one of these headings. The graphics card ID number, which we'll need in the next step will be listed to the left of the heading. Make a note of it.
7. Open a new Terminal window either by clicking on the icon or using the keyboard shortcut Type in the following command into this new Terminal to look up your graphics card's information: sudo lspci -v -s [enter your graphics card's id here]
So you’ve managed to identify your graphics card and pull up its specs. But what does all this technical jargon mean? Let’s break down the most important stuff:
Video RAM or V-RAM refers to a GPU’s temporary storage, onto which image and video files are written before they’re rendered. That’s why you need a GPU with a large V-RAM to render the complicated graphics that you get in modern video games.
When looking at the specs on your computer, V-RAM might be listed as ‘Memory Size’ or another similar term.
Texture Mapping Units, as the name implies, maps textures onto objects. So whenever you see a realistic-looking environment inside a video game, that’s the work of TMUs. TMUs are not only responsible for rendering the look of textures but also their behavior as well (for example, water splashing and rippling out whenever your character jumps in).
The difference between graphics cards with higher TMUs and those with lower TMUs is that the former will render textures on screen much faster. A common misconception is that a higher number of TMUs means better texture quality. In reality, it’s all about the render speed.
Shaders or Shading Units are programs that apply various effects to 2D and 3D objects. This includes hue, saturation, lighting, shadows, blur…etc. which are all the things that add realism to the graphics we see in games and movies.
The more shading units a GPU has, the more nuance and detail it can place in the graphics.
If you’re planning on playing a new game or installing a complex piece of software, then you might be rightfully wondering whether you need to upgrade your graphics card.
To make things easier, we’ve come up with this graphics card upgrade checker to help you come to a decision more easily:
If you’ve been relying on an integrated graphics card up until now, it might be worth investing in an external one, especially if you want to start gaming. Granted, certain e-sports titles like Fortnite can run on certain integrated Intel graphics cards but you’d still be limiting yourself overall.
If you plan on running software such as Blender or Adobe Dimension, an external graphics card is mandatory.
Related Posts:
This is the most important question you need to address. Thankfully it’s easy to determine a graphics card’s compatibility. Simply go on the manufacturer’s website for the software or game in question and peruse through the listed minimum specs. Then compare this with your graphics card’s specs.
If you plan on continuing to play games, we’d recommend getting a GPU with at least 6GB of V-RAM. This should help you satisfy the minimum requirements of most upcoming games for at least another year or so. If you’re keen on future-proofing your PC even more, then go for 8GB.
The same is true if you’re planning on using 3D modeling, video-editing, and illustration software.
And that’s it for this guide! Hopefully, you won’t ever have to wonder ‘what is my GPU?’ ever again, regardless of what operating system you use.
